3D-Laserscanning – Digitale Zwillinge als Grundlage moderner Planung
Warum Laserscanning unverzichtbar geworden ist
Umbauten, Erweiterungen oder Retrofit-Projekte im Anlagenbau und im Gebäudebestand erfordern heute eine Planungsgrundlage, die präziser ist als jede klassische Vermessung. Fehler im Aufmaß führen später zu Störungen im Bauablauf, Mehrkosten und improvisierten Lösungen – besonders in gewachsenen Bestandsstrukturen.
Genau hier setzt das 3D-Laserscanning an.
Durch moderne Lasertechnologie lassen sich bauliche Gegebenheiten vollständig digital erfassen und als exakter 1:1-Zwilling abbilden. Dieser digitale Zwilling wird anschließend Grundlage sämtlicher Planungs-, Konstruktions- und Ausführungsprozesse.
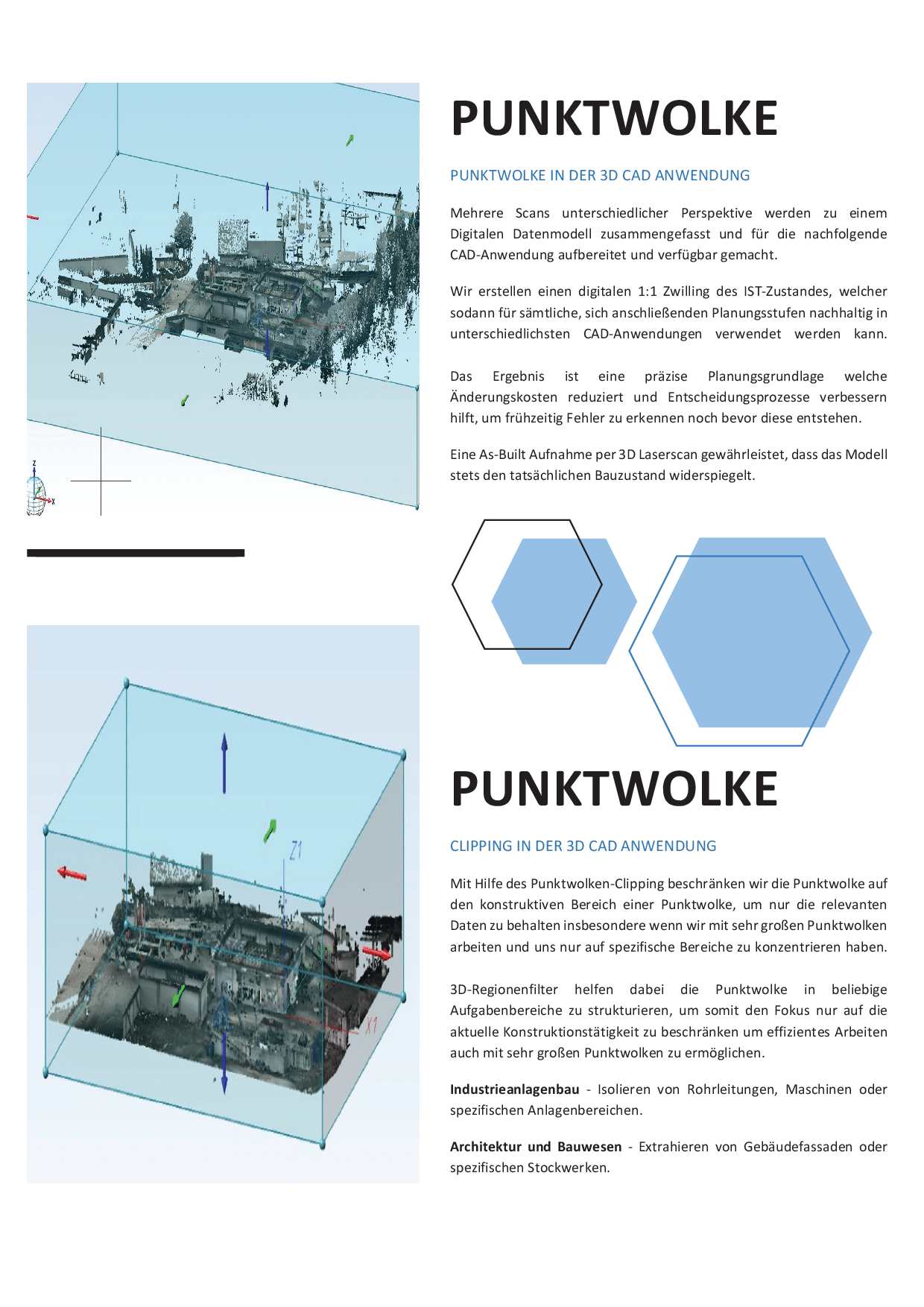
Erzeugung einer präzisen Punktwolke
Mit unserem FARO-Laserscanner erfassen wir die baulichen Strukturen in hoher Dichte und Genauigkeit.
Mehrere Scanpositionen – innen wie außen – werden zu einer zusammenhängenden Punktwolke zusammengeführt. Dadurch entsteht ein vollständiges Abbild des IST-Zustandes, unabhängig von:
- komplexen Geometrien
- schlecht zugänglichen Bereichen
- variierenden Lichtverhältnissen
- umfangreichen technischen Installationen
Die Punktwolke bildet jede Wand, jedes Bauteil, jede Abweichung und jede Unebenheit realitätsgetreu ab.
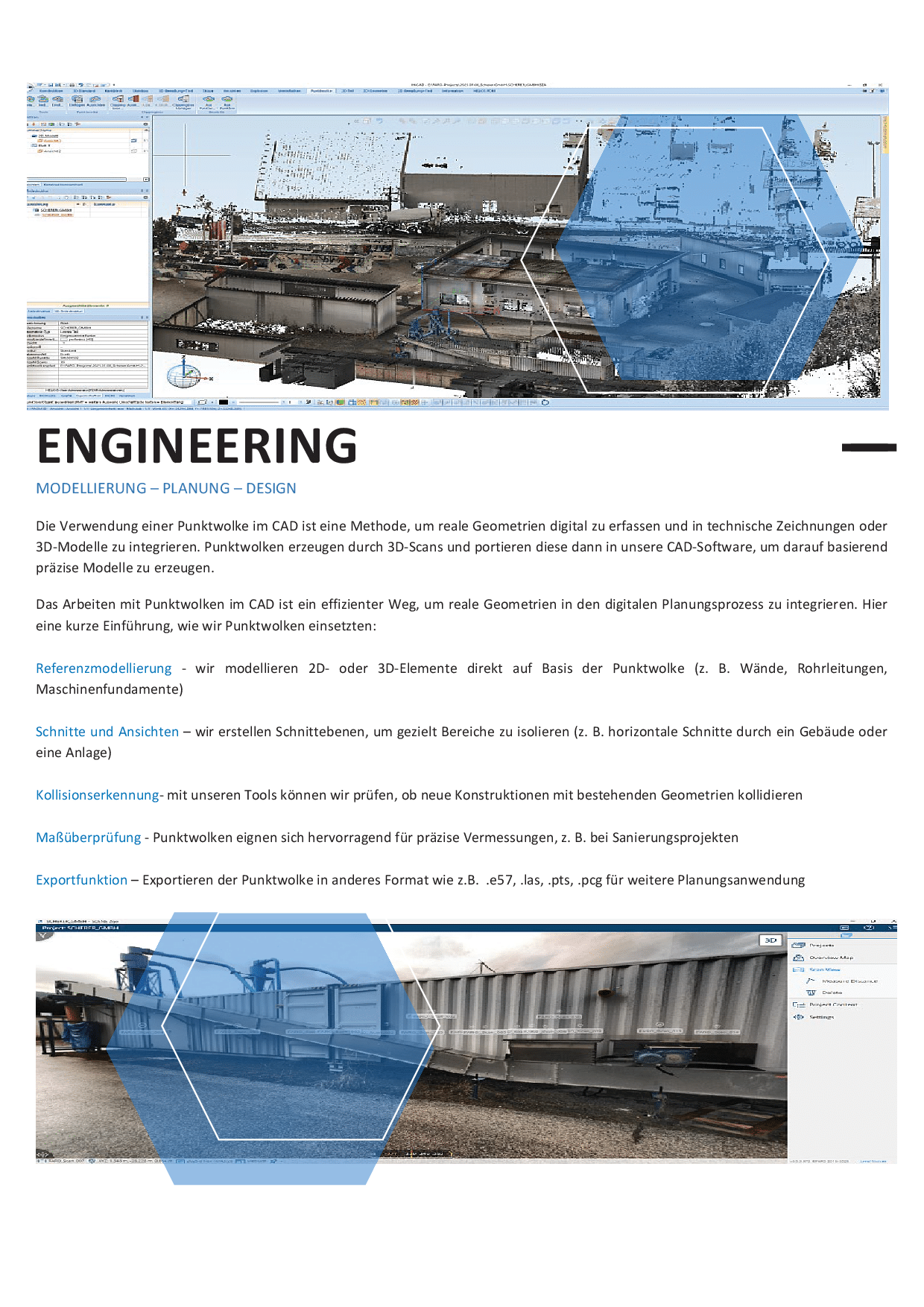
Weiterverarbeitung im CAD-System
Die Punktwolke wird in unsere CAD-Systeme importiert und dient als digitale Grundlage für:
- Referenzmodellierung von Bauteilen, Anlagen und Maschinen
- Ableitung exakter 2D-Bestandspläne
- Erstellen von Schnitten, Ansichten und Höhenrissen
- Kollisionserkennung für neue Konstruktionen
- Maßprüfungen und Toleranzanalysen
- Export für BIM- oder weitere Planungsumgebungen
Damit wird das reale Umfeld vollständig in den digitalen Planungsprozess integriert.
Arbeiten mit großen Punktwolken
Um effizient mit umfangreichen Punktwolken zu arbeiten, verwenden wir:
- Clipping-Funktionen, um nur relevante Bereiche sichtbar zu halten
- 3D-Regionenfilter zur Strukturierung großer Datenmengen
- frei definierte Schnittebenen für zielgerichtetes Konstruieren
- modulare Arbeitsbereiche für Anlagenbau, Architektur und Innenausbau
So können selbst große Industrieanlagen digital bearbeitet werden, ohne dass die Datenmenge den Workflow belastet.
BIM und digitale Projektkoordination
Im Rahmen größerer Vorhaben können Punktwolken direkt in BIM-Projekte integriert werden.
Vorteile:
- alle Gewerke arbeiten auf einer gemeinsamen, fehlerfreien Datengrundlage
- Durchgängigkeit von Planung bis Betrieb
- Vermeidung geometrischer Konflikte bereits in frühen Phasen
- bessere Entscheidungsfindung durch vollständige Transparenz
Für internationale Projekte ist dieser digitale Zwilling oft das zentrale Bindeglied zwischen verschiedenen Teams und Disziplinen.
Einsatzgebiete
Das 3D-Laserscanning findet Anwendung in:
- industriellen Retrofit-Projekten
- Maschinen- und Anlagenbau
- Architektur und Hochbau
- Hallen- und Gebäudebestand
- Umbauten im laufenden Betrieb
- präzisen Aufmaßsituationen mit komplexer Geometrie
Überall dort, wo exakte Bestandsdaten entscheidend sind, bildet der Scan die Basis für eine sichere Planung.
Fazit
Mit moderner 3D-Laserscantechnik schaffen wir eine präzise Datengrundlage für Industrie, Anlagenbau und Bauwesen.
Der digitale Zwilling reduziert Planungsfehler, beschleunigt Entscheidungen und ermöglicht eine reibungslose Zusammenarbeit zwischen allen Projektbeteiligten – unabhängig vom Standort.
In diesem Dokument zeigen wir beispielhaft, wie wir 3D-Laserscanning im industriellen Anlagenbau einsetzen – von der Bestandserfassung über BIM-Koordination bis hin zum As-Built-Modell.
Der Download soll Interessierten einen transparenten Einblick geben, wie wir arbeiten, welche Vorteile entstehen und welchen Mehrwert moderne Scantechnologie in realen Projekten liefert